Time:2025-03-25
Time:2025-03-25
 Source:
Source:
At the recently concluded National Two Sessions, Chinese Premier Li Qiang outlined a clear pathway for green development in the government work report, emphasizing a coordinated approach to "reducing carbon emissions, cutting pollution, expanding green initiatives, and driving economic growth." Pollution control, circular economy, and low-carbon transition have been designated as national strategic priorities.
Driven by China’s dual carbon goals and ecological civilization agenda, the solid waste recycling industry is witnessing a historic transformation—evolving from an "environmental cost" into a "new engine" for green growth. A wave of industrial reform, fueled by technology, capital, and policy support, is already in motion.

With the formulation of the Comprehensive Solid Waste Management Action Plan now on the agenda, policies are integrating "waste recycling" with the "green and low-carbon economy" more deeply than ever before. According to the 2024-2030 Solid Waste Treatment Industry Status and Future Development Trends Analysis Report by China Research Institute, the industry’s market value is expected to reach ¥1.3 trillion by 2025. Meanwhile, green trade regulations such as the global Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) are accelerating the replacement of virgin materials with recycled alternatives in manufacturing.

Against this backdrop, solid waste management is no longer confined to end-of-life disposal but is extending into a full-value chain approach—covering "resource regeneration, product reconstruction, and carbon asset appreciation." This shift is fostering emerging industries such as green construction, renewable energy recycling, and digital carbon management.
Technological Innovation: The Key Lever for Industrial Upgrading
Traditional solid waste treatment methods, primarily reliant on manual sorting, landfilling, and incineration, are being revolutionized by cutting-edge technologies such as AI-based visual recognition, hyperspectral sensing, and intelligent robotic sorting.
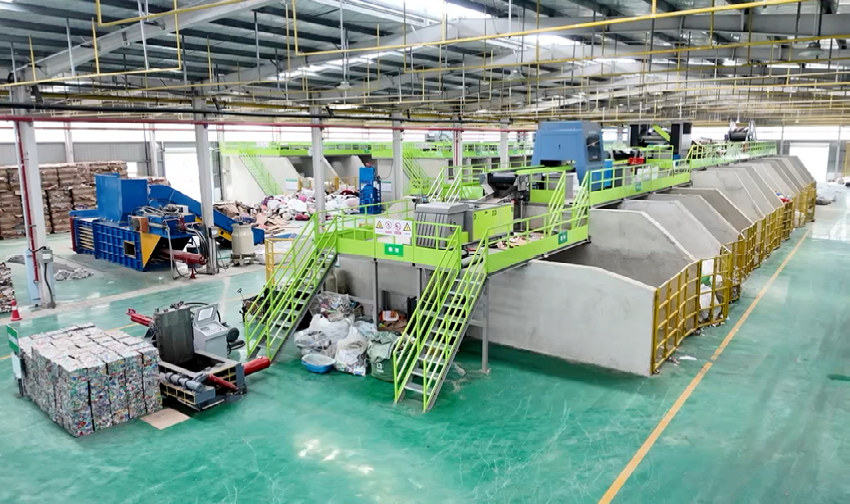

For example, China’s leading waste sorting company, Qinglv Environment, has developed an advanced system combining "crushing + 3D screening + multi-gradient precision sorting (intelligent robotic sorting + optical sorting)." This technology enables the precise separation of construction waste materials, significantly reducing the cost of recycled aggregates per ton.

According to People’s Daily, a demonstration project built by Qinglv Environment in Guangzhou has successfully achieved waste reduction and 100% resource utilization for construction and home renovation waste, showcasing the multiplier effect of technological advancements on industrial efficiency.

The Development of International Markets Has Further Broadened The Industrial Boundary
China’s domestically developed construction waste sorting equipment has entered markets such as Indonesia and Thailand, helping Southeast Asian countries significantly reduce mixed waste treatment costs. Moreover, China’s involvement in setting international standards for recycled aggregates is gradually strengthening its global influence in the field.
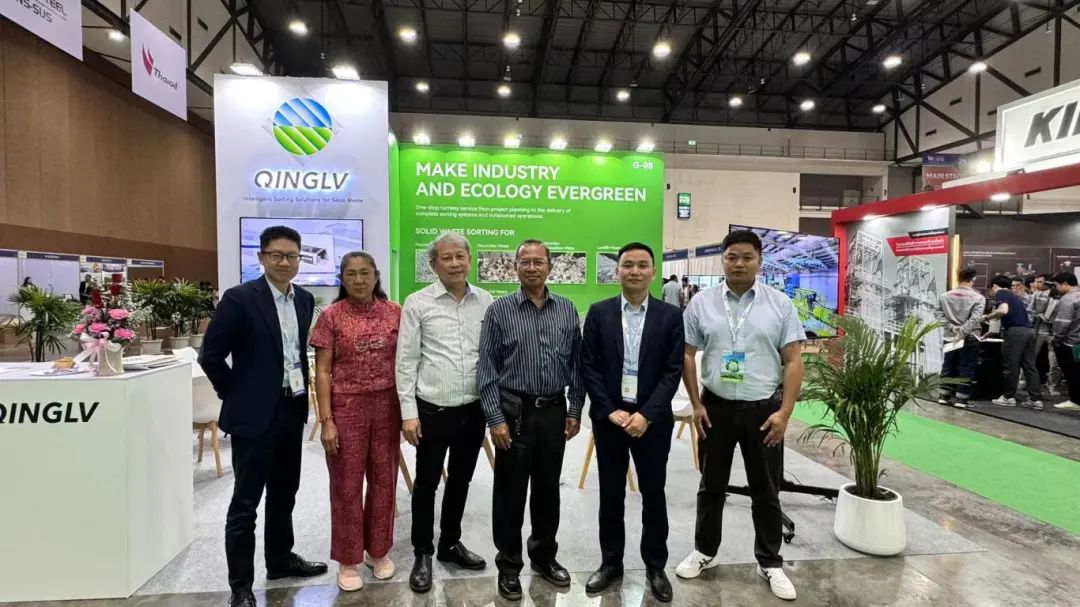


As the EU’s carbon tariff mechanism takes effect, export-oriented enterprises are facing a surge in demand for recycled material certification and carbon footprint management. This has given rise to a new cross-border market opportunity—integrating solid waste recycling technology with carbon credit trading, potentially unlocking a trillion-yuan market.
At the intersection of policy and market forces, the solid waste industry is moving from the periphery to the mainstream. The government work report’s call to "accelerate the development of a green and low-carbon economy" not only reinforces confidence in the industry but also signals a decade of rapid competition in technological leadership, business model innovation, and ecological collaboration.

For enterprises, capitalizing on policy incentives, achieving breakthroughs in core technologies, deepening regional market applications, and leading global standards will be key to gaining a competitive edge in this green revolution. A more efficient and sustainable growth model is already taking shape.














 Prev
Prev